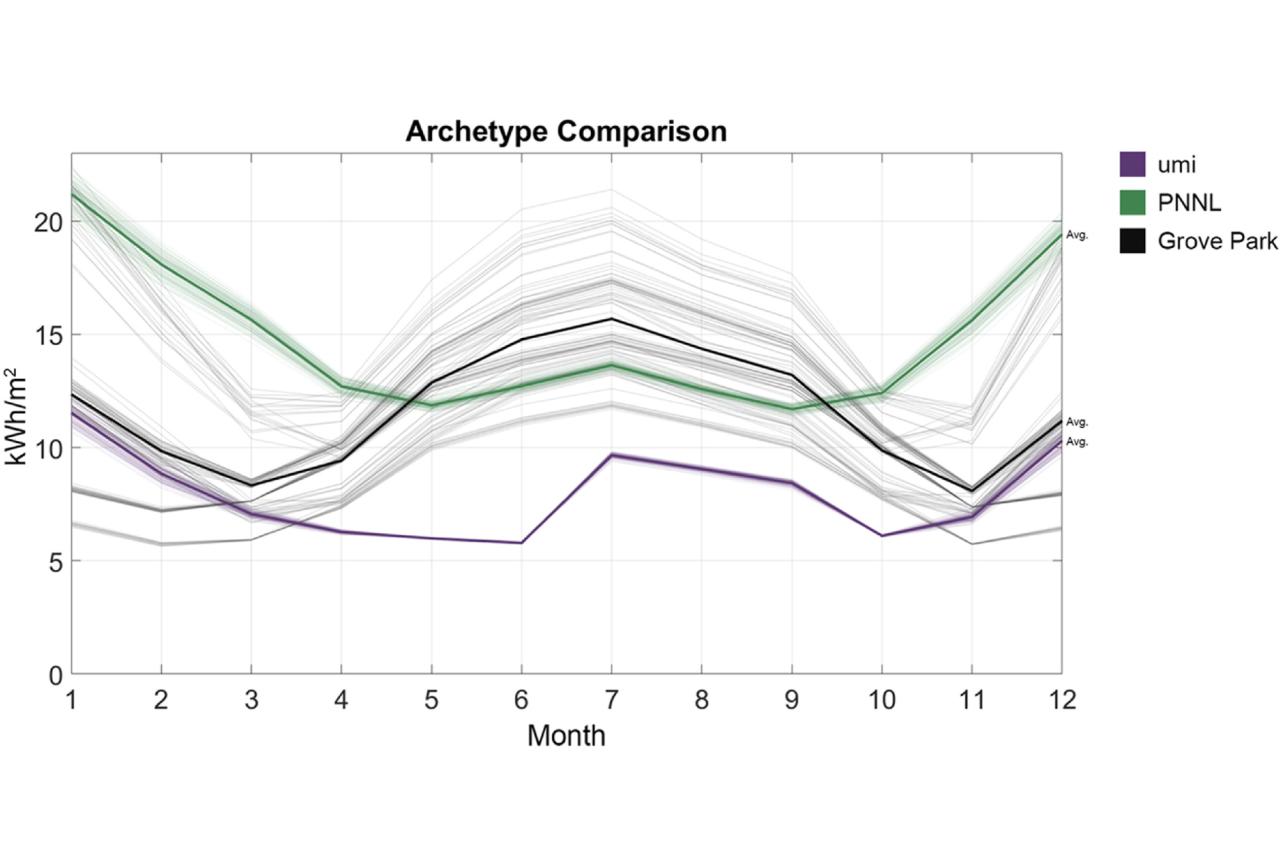
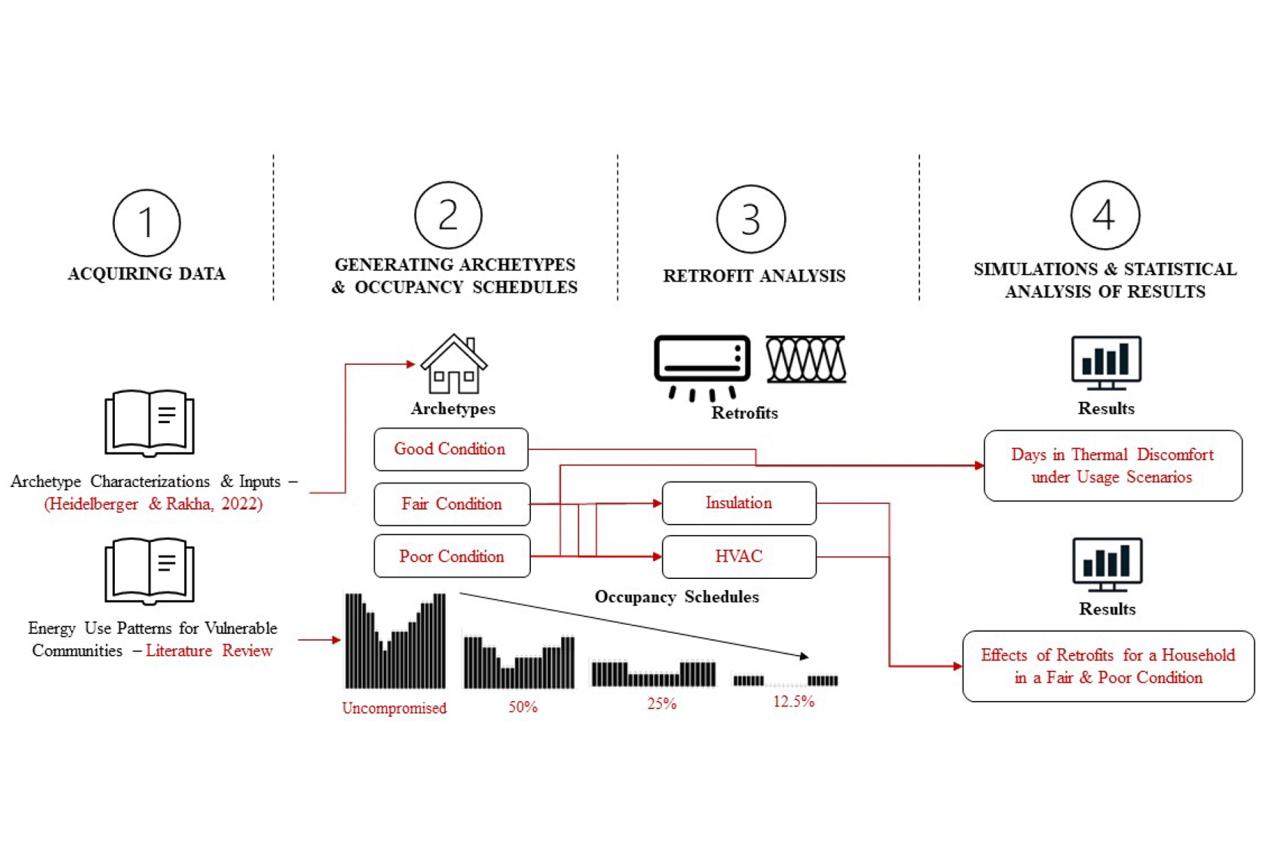
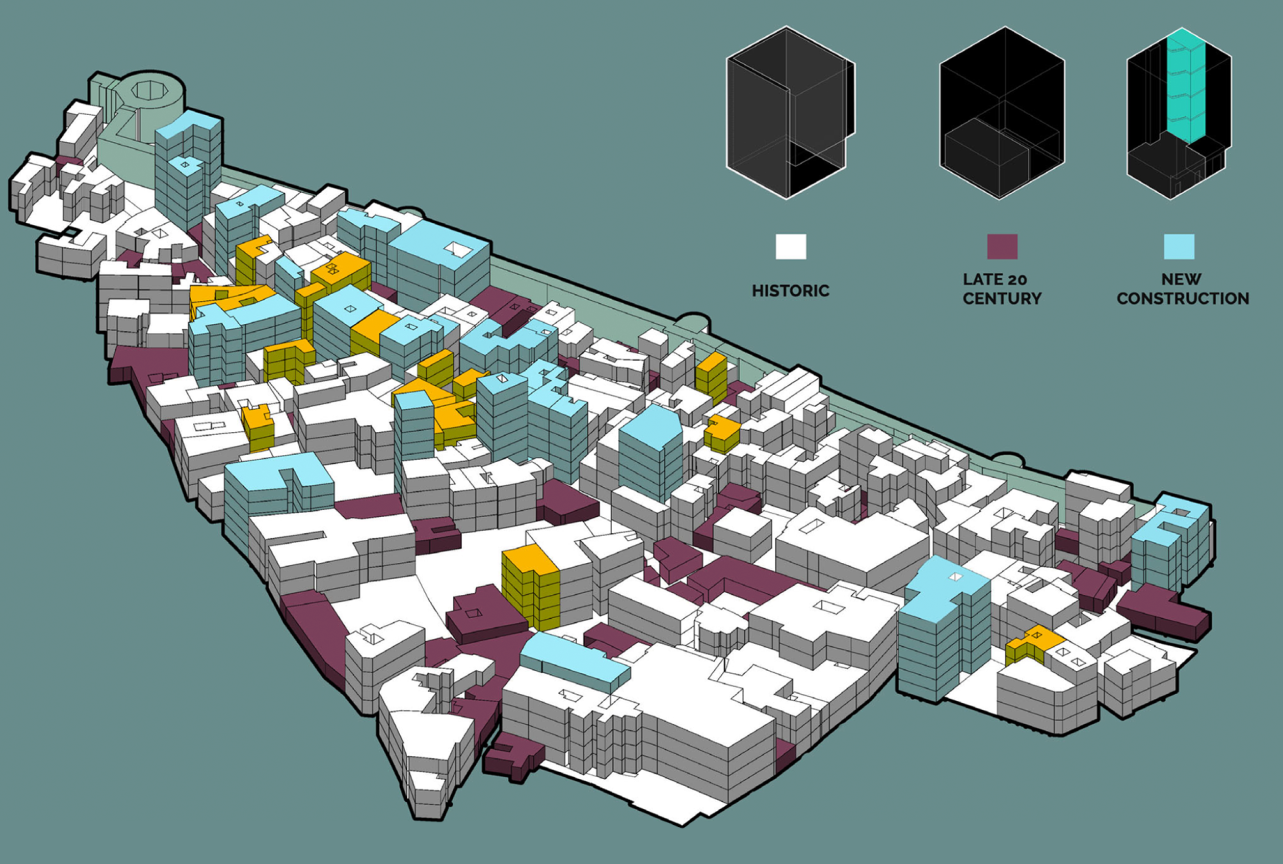
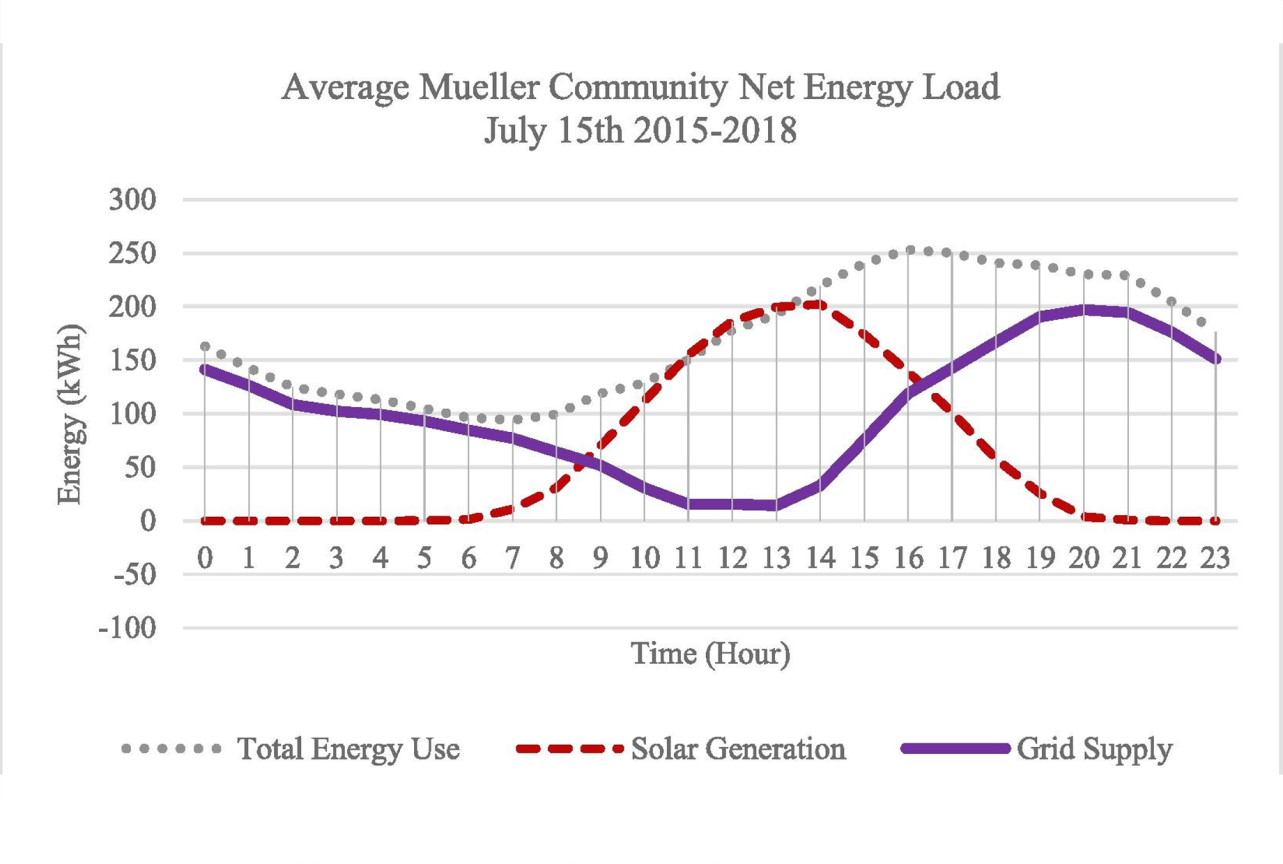
Community Analytics
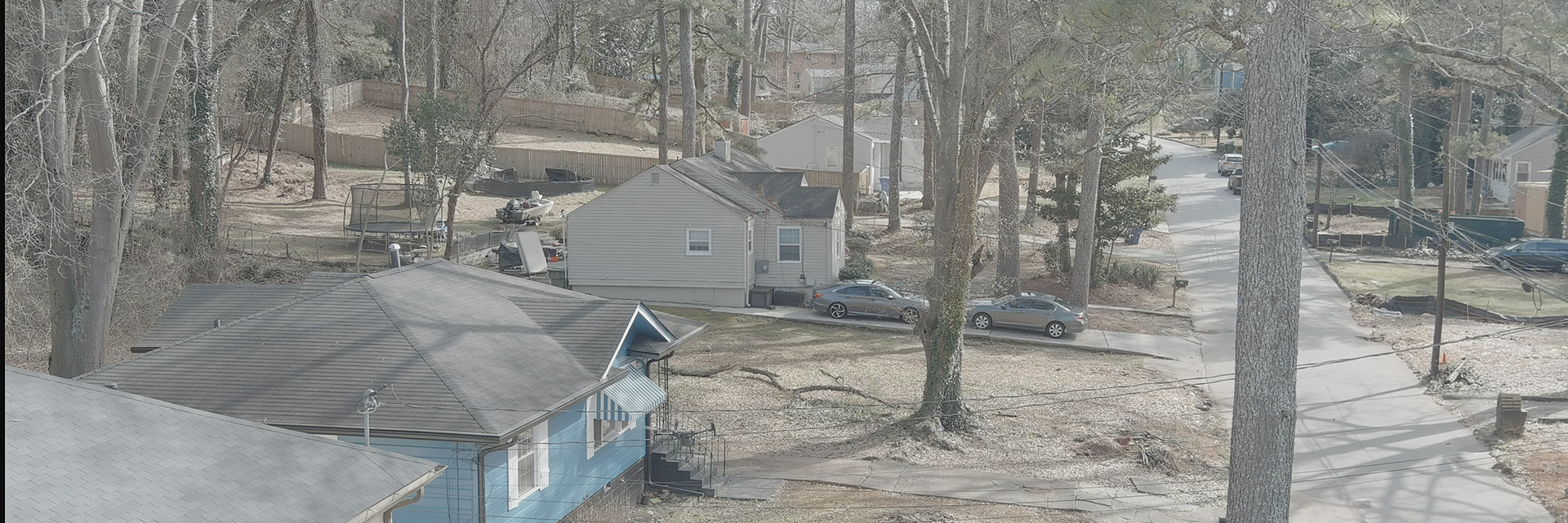
Urban areas use approximately 70% of the world's energy and are among the highest contributors to global CO2 emissions. One method of addressing current and future energy use and emissions in cities is Urban Building Energy Modeling (UBEM). Building Performance Simulation (BPS) has a history of using standard inputs that introduce bias to the models and fail to account for a variety of cultural, racial, and economic backgrounds. Most current data sources used in UBEM are designed around ideal urban settings and do not account for the realities of majority-minority and low-income neighborhoods. Including socioeconomic factors helps produce representative and equitable UBEM in all areas, but is especially important in low resource communities. The Community Analytics’ research argues for the consideration and inclusion of demographic and socioeconomic factors in all building and urban simulation studies. We highlight critical obstacles and key parameters related to people, envelope, and systems that are more sensitive in the context of racial, income, and resource inequalities.