Performance Informatics
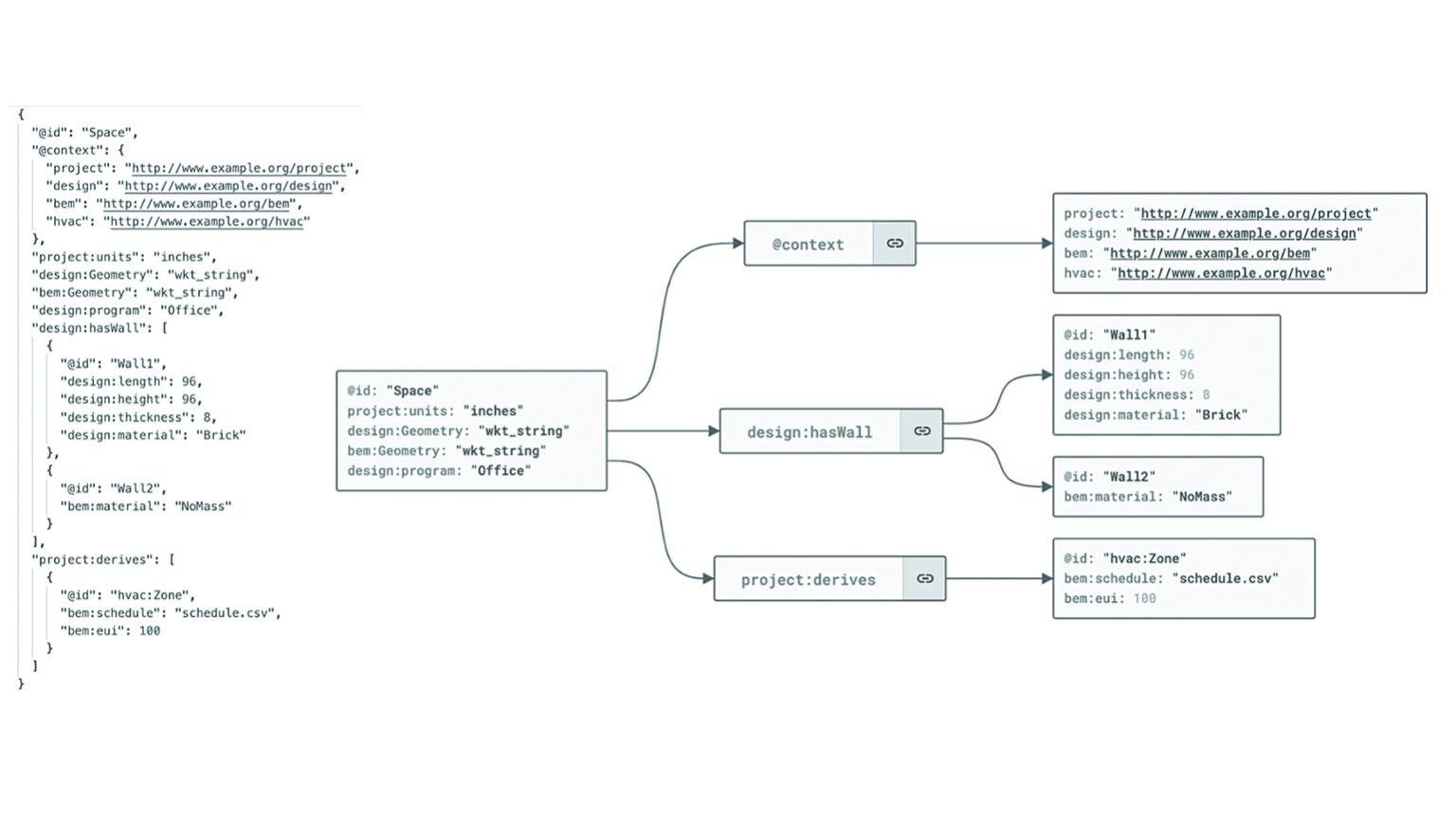
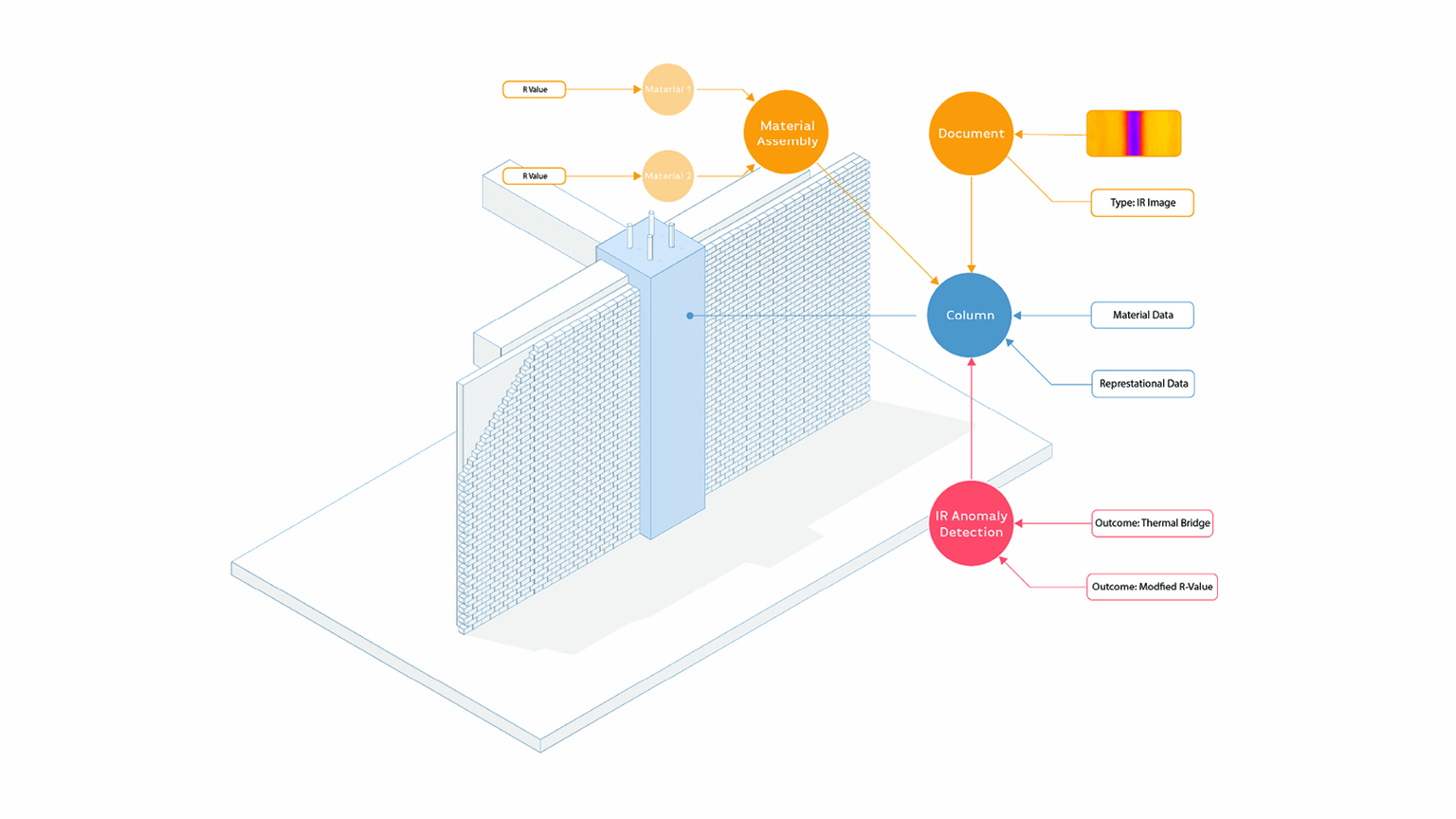
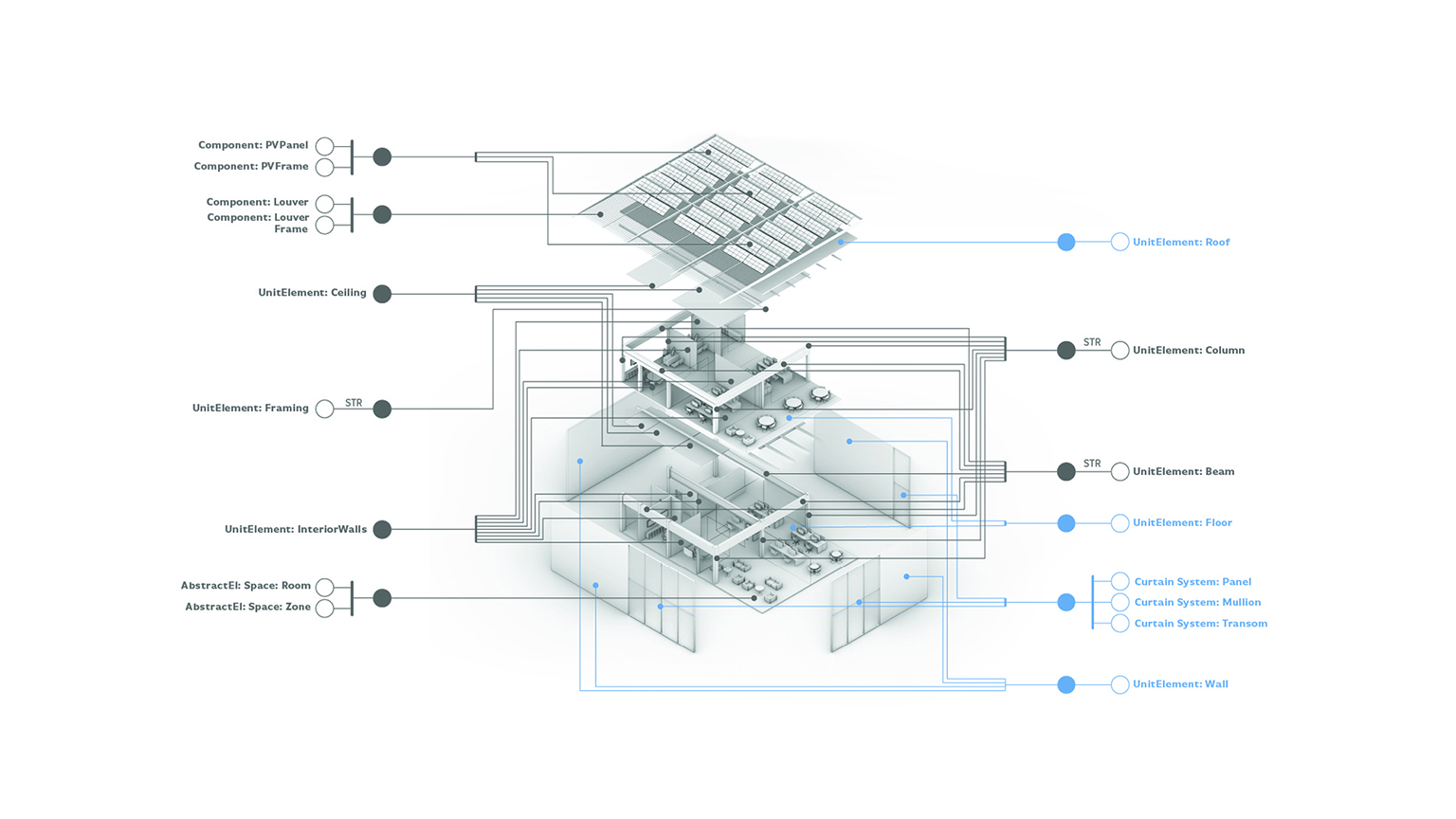
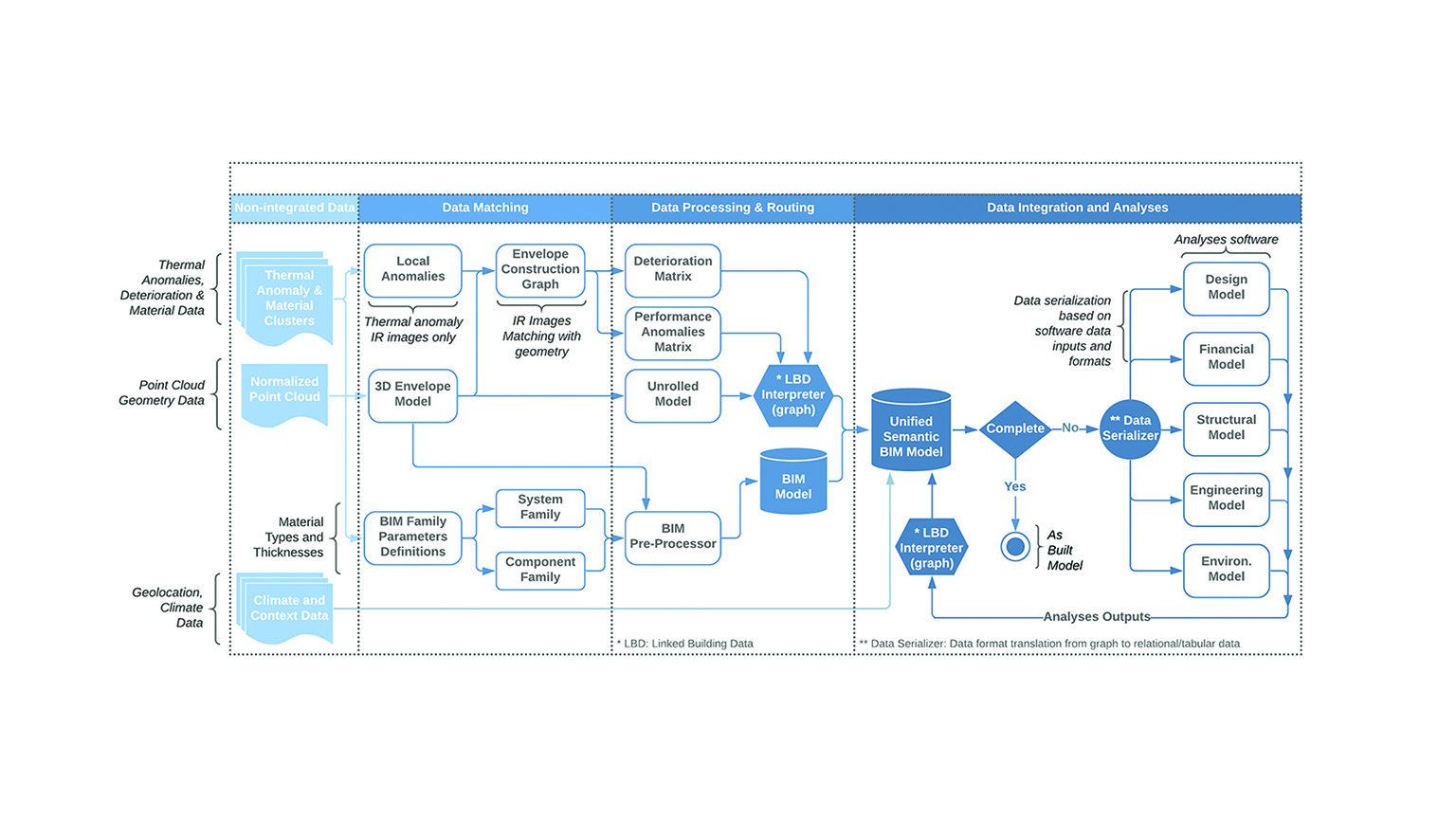
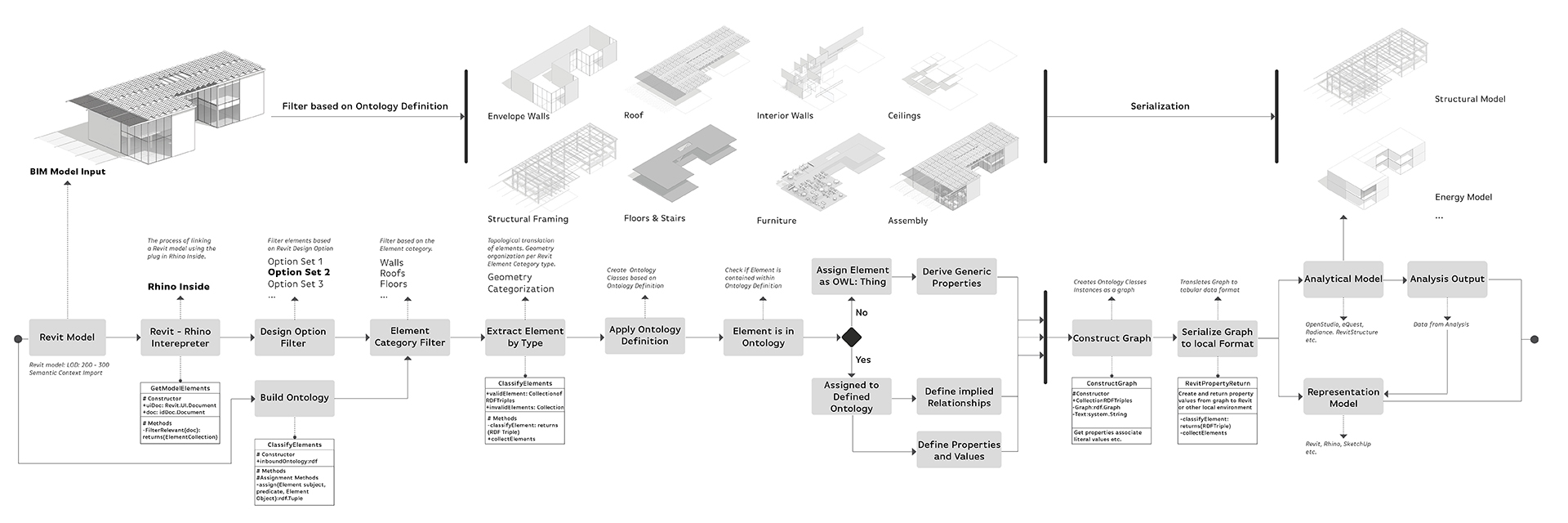
The scope of the Performance Informatics group is investigating representations of built environment interrelated and nested data. We seek to enable practitioners in making better design decisions through the use of data available to them. This is achieved by linking existing tools with semantically rich data structures to industry standard tools, creating a data driven paradigm of design computation within native working environments.
Existing tools are constrained by the limits of their own semantic context. This lack of a shared context makes the exchange of data between stakeholders and collaborators more difficult than is necessary, given state-of-the-art technologies. This work continues from other Linked Building Data (LBD) projects such as the Building Topology Ontology (BOT) and other projects such as BRICK that provide a flexible means of representing and exchanging information, without the necessity of losing critical discipline specific data.